NFC wireless charging is the most convenient way to charge the battery of small devices such as earbuds, smart watches and styluses: NFC operates through a small antenna which is tolerant of misalignment, and it provides for simple communication alongside the charging function, to keep the charging cradle updated with the state of charge and other device information.
But the big drawback of NFC charging in the past has been speed: the low power received at the listener (charged device) has meant that it took too long to charge even a small battery.
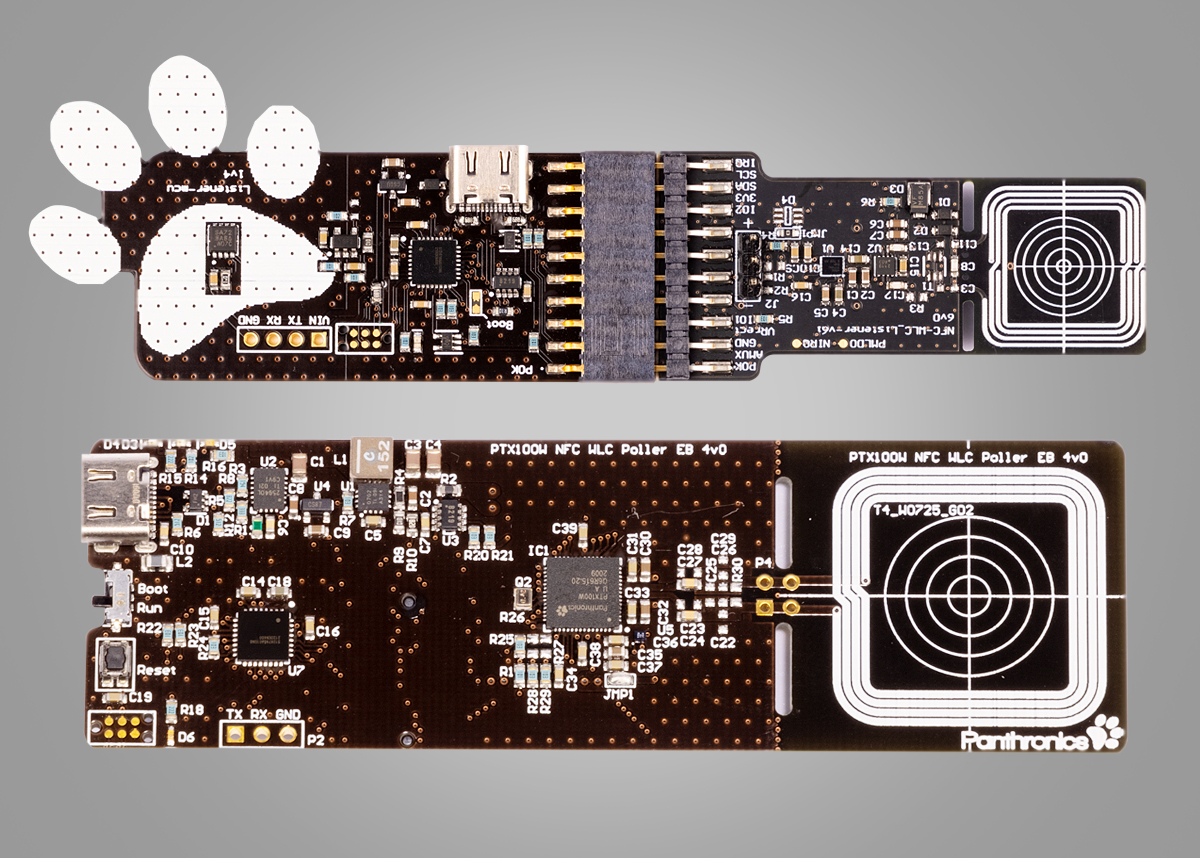
The PTX100W NFC charger IC from Panthronics puts this problem to bed. The PTX100W, based on Panthronics’ patented sine wave silicon architecture, produces much higher output power than competing square wave NFC chargers. The sine wave architecture also enables the elimination of the EMC filter in conventional systems, so antenna matching impedance can be cut in half, and power losses attributable to external components reduced.
The result in the Panthronics system is as much as 1W received power at the listener, and much faster charging. And because the Panthronics solution requires fewer external components, bill-of-materials costs are lower and the smaller board footprint saves space.
Implementation of the PTX100W charger is made much easier than designers might expect because Panthronics supplies a complete reference design system for both the poller (charging side) and the listener.
(All images sourced from Panthronics)
You must be signed in to post a comment.
Comments
No comments yet